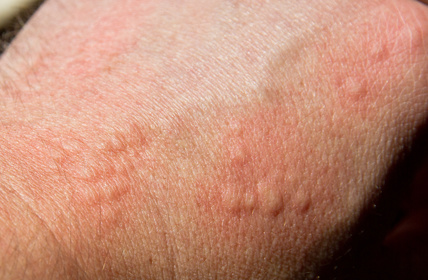
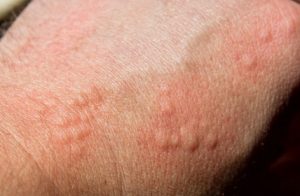
Scabies is a contagious skin condition characterized by itching. It is caused by microscopic parasites scientifically known as Sarcoptes scabiei. These parasites are also commonly called the “itch mite.” Bed bugs are also parasites that suck the blood of birds and mammals, including humans. Two species of the insect Cimex are responsible for bed bug bites.
If you feel an itching sensation, you might be confused about whether it’s scabies’ bite or a bed bug bite. In this article, we will give you a comparative analysis of both kinds of parasites, what do they and their bites look like, how they can be treated and what preventive measures can be taken for their treatment.
 What do Scabies mite and Bed Bugs look like?
What do Scabies mite and Bed Bugs look like?
The Scabies’ mite Sarcoptes scabiei is a tiny arthropod. It is an eight-legged microscopic parasite. The naked eye cannot detect the “itch mite.” It is often confused with a bed bug bite. This mite has the same lineage as spiders, ticks, etc. It causes an infestation, not an infection on the human body. Sarcoptes feeds on blood from the inside of the body, since it burrows in the skin layer.
Bed bugs are white to reddish-brown in color. Once fed, they turn into a rusty-red shade. They have an oval-shaped body and are visible to the naked eye on close examination. Bed bugs feed on blood from outside. They usually bite at night and then return to their hiding spots, including mattresses, nooks, and crannies.
Do all Scabies’ mite or Bed Bugs Bite?
In most types of bites, the female is responsible because it needs blood for its life cycle. In the case of scabies and bed bugs, it differs due to the type of parasite.
The female Scabies’ mite lays eggs by “burrowing” under the dermis skin layer. It lays 2-3 eggs every day. The incubation period of Sarcoptes mite is 2-6 weeks after infestation. The female mite feeds on the blood. The larvae hatching from the eggs crawl into the skin’s hair follicles to feed and molt. The itch mite usually burrows in warm, moist areas of the skin. It can be found on wrists, joint areas and finger webs, etc. These parasites cause red white grayish lines on the skin. They live on human blood, therefore building burrows in the dermis layer of skin.
Both the male and female Bed bugs bite. A female bed bug mates via traumatic insemination with the male. The female on average can lay up to 1-12 eggs per day but usually lays 5-7 eggs per week. It is dependent on the blood for reproduction. Bed bugs usually bite during the night and hide during the day. They bite on the exposed area of skin like shoulders, arms, legs, back and face. Bed bugs cause swollen bumps or welts on the skin. They feed on blood and return to their hiding spot.
Since both types are parasites, therefore, they need blood as an essential part of their reproductive life cycle. This does not always affect their survival rate though.
Does a Scabies’ mite or Bed Bug bite hurt?
The bite of both the “itch mite” and bed bugs causes intense itching, uncomfortable sensation and a constant urge to scratch. The itching characteristic often leads to the confusion between these two different types of bites. The painful bites lead to a disturbed sleeping pattern, poor work performance, etc.
What does a Scabies’ or Bed Bug bite do? Is it harmful?
Both types of bites can cause harmful conditions if left untreated for too long. It is better to identify if the bite is from Sarcoptes or a bed bug. This can help in getting the probable treatment.
Scabies is itself an uncomfortable skin condition. It is contagious, thus any person with Scabies can cause the disease to another. A Scabies’ mite can bite and cause the following symptoms:
- Intense Itching

- Rashes, red bumps or bites
- Lesions or papules
- Sores due to scratching
- Irritability, fatigue or fever (in severe cases)
A bed bug’s bite can cause the following:
- Skin rashes or welts
- Psychological effects (anxiety, stress or insomnia)
- Anemia
- Anaphylaxis
These symptoms vary on the basis of the intensity of infestation. If the person has a chronic or prolonged period of infestation, then these symptoms become more severe.
Also Read: WHAT DO BED BUGS LOOK LIKE?
Preventive Measures for Scabies or Bedbugs:
As the saying goes, it is better to prevent a disease rather than cure it. This is because preventive measures can help you in staying healthy. Thus, we have listed some important precautions below:
-Always air your bed sheets, mattresses, and foams. Wash and dry all clothes, towels or bedding with hot water and high heat.
-Keep your bedrooms and furnishings clean, free of dust and moisture. Vacuum all nooks and crevices, mats, rugs, carpets and upholstered furniture. This will reduce the number of bed bugs if any.
-Take a bath on a daily basis. A clean body is a key to maintaining your health.
-Avoid using second-hand furnishings. In case you buy any second-hand furniture, always check for bed bugs. Get rid of them if there are any.
-In the case of bed bugs, you can call pest controllers to identify and remove bed bugs from your house. Heat is an essential factor in getting rid of these pests.
–Scabies is a skin condition, therefore, consult a dermatologist for treatment. Do not expose a patient with Scabies to another human, since the disease is contagious.
-Do not use topical solutions like creams, lotions or gels for itching, without prescription for treating these bites.
Verdict
Even with all the cleanliness and health measures, there is no foolproof method to prevent Scabies or bed bugs. But it is always better to take precautions and prevent the disease.
Hence, Scabies’ mites and Bed bugs are different from each other. We have listed the factors that can help identify the variant nature of their bites, reproductive cycle, and helpful preventions.
You might also like: BABY BEDBUGS – WHAT DO BABY BEDBUGS LOOK LIKE?